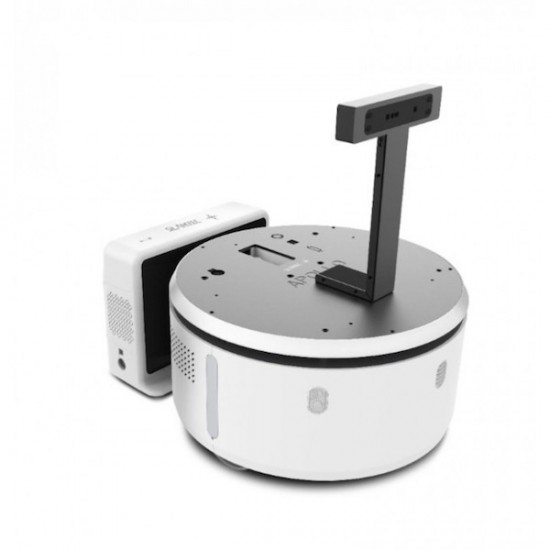

Presentation and applications of the mobile base Apollo
Warning: At the moment, Apollo hasn’t got the CE certificate and can thus only be used in prototype projects in R&D, labs or other institutes of higher education.
The mobile robot Apollo is one of the best mobile bases available for public applications. He was designed to move autonomously in public places and to be capable of facing numerous simple and complex situations. The mobile base Apollo is a development platform that is ready to be used. You will be able to use its highly developed navigation features with the unpacking of Apollo. It can execute its mapping function (real-time cartography), autonomous navigation and avoiding obstacles almost immediately.
The documentation supplied by the manufacturer SLAMTEC is simple and concise. Their quick startup guide and their user’s guide will ensure that you can quickly work with your mobile base Apollo, even if you’re not an engineer, nor a developer nor a real technology lover.
The mobile robot Apollo is upgradeable, that’s one of its advantages. You can easily install a touch screen on top of his platform, a robotic arm, a second or third platform, a camera, other sensors, etc.
On top of that, the Software SLAMTEC SDK allows you to develop third-party applications for the robot Apollo.
The mobile base Apollo can become whatever you wish for with its minimalist and elegant design and its flexibility to best fulfill the task you have in mind: guide, in-house courier (max. load 35kg), reception robot, sales consultant, etc.
Features of the mobile robot base Apollo
Real-time recognition of its environment
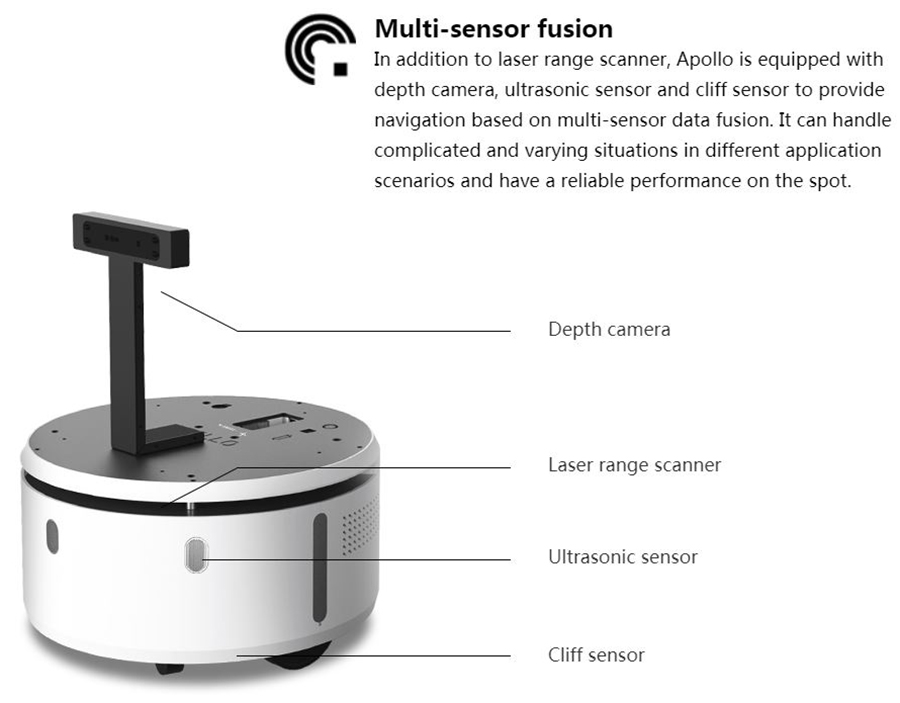
Apollo is equipped with an Scanner Laser 360° RPlidar A2 that can see and measure up to 15m of distance.

The RPlidar A2 uses a measurement system based on triangulation laser as well as the OPTMAG technology, both developed by the manufacturer SLAMTEC. The RPLidar has a significantly longer life than others without losing its accuracy or efficiency.
The mobile base Apollo also has a depth camera, situated around 30cm higher than the RPLidar. This depth camera allows the robot to detect obstacles that the Lidar can’t detect (because lower situated), e.g. the edge of a table. To detect near obstacles, SLAMTEC has integrated three ultrasonic distance sensors detecting obstacles that are 40 cm or less away from the robot.
Apollo is also equipped with three cliff sensors. They are situated under the robot and are able to detect holes and drops with a minimum depth of 5 cm and prevent the robot from falling from e.g. the top of stairs.

Autonomous real-time cartography for navigation and localisation
Apart from his numerous sensors that guarantee safety and autonomy, the Apollo robot was designed with a lower barycenter offering a better stability and more safety for his environment. It can even overcome small elevations (watch out for cables!).
Different than other robots, Apollo doesn’t need other added external elements (GPS beacons) to use its navigation and localisation feature (except in extraordinary environment).
Apollo can map in real time (mapping). It uses the SharpEdge technology to create extremely precise maps and layouts (with a resolution of up to 5 cm without accumulating errors).
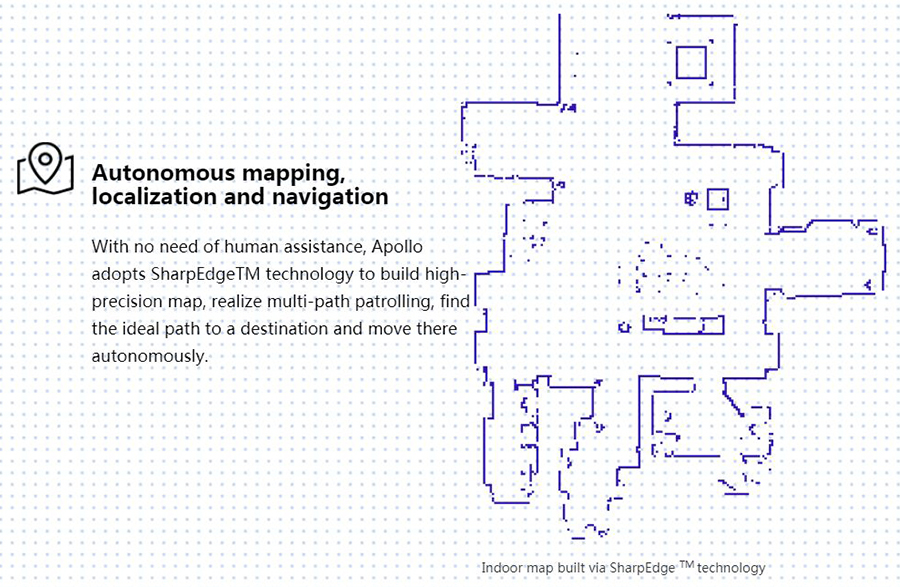
The user can also create virtual tracks and walls for the robot Apollo. The creation of virtual tracks could e.g. be useful for round tours if the robot is used in a mission of surveillance. The virtual tracks allow the robot to use predefined paths to move between two fixed points and it can thus e.g only use selected hallways in a company. The virtual walls created in the software RoboStudio by SLAMTEC work as a barrier the robot can’t cross. The user can easily limit the coverage area (useful for large areas such as airports or commercial centers).

Finding the shortest way
Thanks to its D* dynamic algorithm allowing Apollo to find the shortest way in real time, it is able to move autonomously to its destination using the shortest way.
Re-Routing
Apollo can dynamically change its way in order to arrive at a destination (e.g. if there is an object that blocks the route) thanks to its many different sensors. It can also autonomously relocate its position in an environment if he has been moved for example.
Using and programming the robot with the software RoboStudio
Once the software RoboStudio is installed (online available for free), the user has access to the data collected by different sensors, can visualise the maps created by Apollo, create virtual tracks and walls, program the robot, supervise it or give orders. The interface is user-friendly and the software offers numerous features including the use of software extensions.
Development of third-party applications
The SDK SLAMWARE of SLAMTEC allows the development of third-party applications including iOS and Android for the robot Apollo. SLAMWARE is a modular navigation and localisation system that integrates simultaneous localisation and cartography (SLAM) based on the RPLidar and its feature of finding the corresponding way. The SDK SLAMWARE allows the development of new features based on the SLAMWARE system and third-party applications to interact with the robot.
Autonomous charging of the battery
The mobile robot Apollo can join its charging base and then be charged on its own. According to the default settings, it joins its base when the battery is less than 30% but this setting can easily be changed.

Data fusion
The data fusion allows the robot Apollo to use all of its sensors for autonomous navigation. It can avoid each obstacle detected by a sensor to navigate safely.
Optional features
Autonomous mapping of several floors
Apollo can map a building with several floors and create links between each floor. This can be useful for organising an emergency evacuation or the navigation of people in commercial centers or airports.
Autonomous use of elevators
Apollo can use elevators that are controlled by WiFi autonomously by sending them orders via a WiFi network. It can enter the elevator, make it move (only by using WiFi), detect at which floor the elevator is at the moment and leave the elevator at its destination.
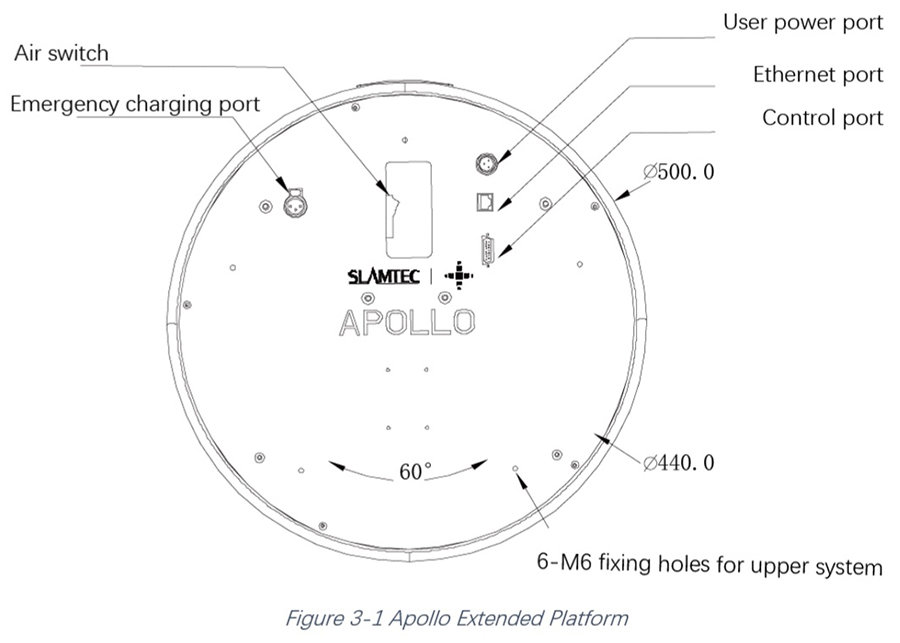
Technical specifications of the mobile base Apollo
Warning: At the moment, Apollo hasn’t got the CE certificate and can thus only be used in prototype projects in R&D, labs or other institutes of higher education.
- Version of the robot: Apollo A2M11 Series
- Main features: localisation and navigation SLAM, autonomous mapping of several floors (option), autonomous use of elevators (option)
- Weight and dimensions:
- Diameter: 500 mm (±10 mm)
- Height: 270 mm (±10 mm) (sans accessoires)
- Weight: environ 40 kg
- Maximum load : 35 kg
- Specification of the sensors:
- RPlidar :
- Maximum coverage area (on a surface with a reflectivity of 90%): 15 m
- Ultrasonic sensors:
- Quantity: 3
- Maximum distance to detect: 40 cm
- Depth Camera:
- Maximum distance to detect: 1.30 m
- Maximum view angle: 45°x 35° (width x height)
- Drop sensors:
- Quantity: 3
- Minimum depth to detect: 5 cm
- Specifications of the cartography:
- Resolution of the maps: 5 cm
- Maximum surface of a map: 150 m x 150 m
- Movement:
- Maximum speed: 0.7 m/sec
- Maximum slope: can’t move on slopes
- Interfaces :
- Hardware interfaces:
- Ethernet : 10/100 Mbps
- Control interface: interface with 15 pins
- Power supply: 20-25.2V 5A Max
- Software interfaces:
- SLAMWARE™ : Windows/iOS/Android/Linux
- Operating life of the battery:
- Operating time: > 12 h
- Slow discharge while in stand-by: < 25 W
- Battery lifetime: after 300 cycles of utilisation/recharging: 60%
- Autonomous charging of the battery:
- Charging base:
- Input voltage: 220~240 VAC
- Output voltage: 25.2V 10A
- Maximum charging time: 5h30
- Operating environment:
- Operating temperature: -10℃~ 40℃
- Operating humidity: 30%~ 70%
